
Tasmanian feral deer numbers shocking
An aerial survey of Tasmania has revealed populations of feral deer in that state are much worse than first thought and demand action.

An aerial survey of Tasmania has revealed populations of feral deer in that state are much worse than first thought and demand action.

Our report into the ethical considerations of using 1080 to control feral animals finds conservation benefits necessitate its use until an alternative is available.
The coronavirus pandemic has shown the need to act hard and fast when new diseases emerge, the same approach has to be taken on invasive species.

Our joint report with Monash University reveals environmentally destructive ants, bees and wasps could be hitching a ride into Australia on an international bug superhighway.

We’re looking for people to seek out and snap ants, bees and wasps in their neighbourhood. For every QuestaGame find, $1 is donated to the Invasive Species Council.

Feral futures 2051 is the theme of the next Australasian Vertebrate Pest Conference, which is being held in Melbourne 4-7 May 2020.

We’ve teamed up with QuestaGame to launch a month-long ‘BonANTza’ eco-hunt in the Cairns region with great prizes to be won.
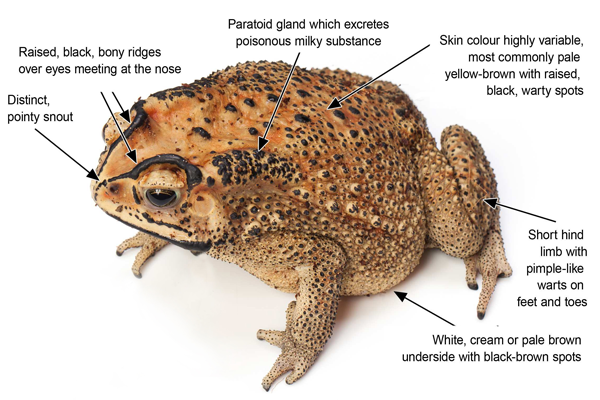

The Australian government has drawn up a hit list of overseas environmental invaders we need to keep out of the country.

Delegates from Australia, New Zealand, the US, Canada and Mexico made first ever biosecurity symposium a smashing success.

Invasive species are one of the biggest drivers of environmental loss in Australia, and threaten our native animals and plants more than any other single factor.

The long-time host of ABC’s Gardening Australia, Costa Georgiadis, will be the official MC of the inaugural 2019 Australian Biosecurity Symposium.

An analysis by 12 ecologists has found that invasive species are the most prevalent threat to Australia’s native plants and animals – impacting 1257 nationally listed threatened species, 82% of the total.

The Gold Coast will be abuzz with all things biosecurity on 12-13 June 2019, when government, industry and other interested parties unite for the inaugural Australian Biosecurity Symposium.

A team of James Cook University scientists is beginning work on cutting-edge ways to repel biosecurity invaders from Australia’s northern shores.

The Australian Senate has announced an inquiry into the growing impacts from feral deer, pigs and goats and to prevent problems worsening for the natural environment, community and farmers.

An aerial survey of Tasmania has revealed populations of feral deer in that state are much worse than first thought and demand action.

Our report into the ethical considerations of using 1080 to control feral animals finds conservation benefits necessitate its use until an alternative is available.

The coronavirus pandemic has shown the need to act hard and fast when new diseases emerge, the same approach has to be taken on invasive species.

Our joint report with Monash University reveals environmentally destructive ants, bees and wasps could be hitching a ride into Australia on an international bug superhighway.

We’re looking for people to seek out and snap ants, bees and wasps in their neighbourhood. For every QuestaGame find, $1 is donated to the Invasive Species Council.

Feral futures 2051 is the theme of the next Australasian Vertebrate Pest Conference, which is being held in Melbourne 4-7 May 2020.

We’ve teamed up with QuestaGame to launch a month-long ‘BonANTza’ eco-hunt in the Cairns region with great prizes to be won.

The Australian government has drawn up a hit list of overseas environmental invaders we need to keep out of the country.

Delegates from Australia, New Zealand, the US, Canada and Mexico made first ever biosecurity symposium a smashing success.

Invasive species are one of the biggest drivers of environmental loss in Australia, and threaten our native animals and plants more than any other single factor.

The long-time host of ABC’s Gardening Australia, Costa Georgiadis, will be the official MC of the inaugural 2019 Australian Biosecurity Symposium.

An analysis by 12 ecologists has found that invasive species are the most prevalent threat to Australia’s native plants and animals – impacting 1257 nationally listed threatened species, 82% of the total.

The Gold Coast will be abuzz with all things biosecurity on 12-13 June 2019, when government, industry and other interested parties unite for the inaugural Australian Biosecurity Symposium.

A team of James Cook University scientists is beginning work on cutting-edge ways to repel biosecurity invaders from Australia’s northern shores.

The Australian Senate has announced an inquiry into the growing impacts from feral deer, pigs and goats and to prevent problems worsening for the natural environment, community and farmers.

An aerial survey of Tasmania has revealed populations of feral deer in that state are much worse than first thought and demand action.

Our report into the ethical considerations of using 1080 to control feral animals finds conservation benefits necessitate its use until an alternative is available.

The coronavirus pandemic has shown the need to act hard and fast when new diseases emerge, the same approach has to be taken on invasive species.

Our joint report with Monash University reveals environmentally destructive ants, bees and wasps could be hitching a ride into Australia on an international bug superhighway.

We’re looking for people to seek out and snap ants, bees and wasps in their neighbourhood. For every QuestaGame find, $1 is donated to the Invasive Species Council.

Feral futures 2051 is the theme of the next Australasian Vertebrate Pest Conference, which is being held in Melbourne 4-7 May 2020.

We’ve teamed up with QuestaGame to launch a month-long ‘BonANTza’ eco-hunt in the Cairns region with great prizes to be won.

The Australian government has drawn up a hit list of overseas environmental invaders we need to keep out of the country.

Delegates from Australia, New Zealand, the US, Canada and Mexico made first ever biosecurity symposium a smashing success.

Invasive species are one of the biggest drivers of environmental loss in Australia, and threaten our native animals and plants more than any other single factor.

The long-time host of ABC’s Gardening Australia, Costa Georgiadis, will be the official MC of the inaugural 2019 Australian Biosecurity Symposium.

An analysis by 12 ecologists has found that invasive species are the most prevalent threat to Australia’s native plants and animals – impacting 1257 nationally listed threatened species, 82% of the total.

The Gold Coast will be abuzz with all things biosecurity on 12-13 June 2019, when government, industry and other interested parties unite for the inaugural Australian Biosecurity Symposium.

A team of James Cook University scientists is beginning work on cutting-edge ways to repel biosecurity invaders from Australia’s northern shores.

The Australian Senate has announced an inquiry into the growing impacts from feral deer, pigs and goats and to prevent problems worsening for the natural environment, community and farmers.
Get our blog the Feral Herald delivered to your inbox.
Our protected areas are being trashed, trampled, choked and polluted by an onslaught of invaders. Invasive species are already the overwhelming driver of our animal extinction rate, and are expected to cause 75 of the next 100 extinctions.
But you can help to turn this around and create a wildlife revival in Australia.
From numbats to night parrots, a tax-deductible donation today can help defend our wildlife against the threat of invasive weeds, predators, and diseases.
As the only national advocacy environment group dedicated to stopping this mega threat, your gift will make a big difference.
A silent crisis is unfolding across Australia. Every year, billions of native animals are hunted and killed by cats and foxes. Fire ants continue to spread and threaten human health. And the deadly strain of bird flu looms on the horizon. Your donation today will be used to put the invasive species threat in the media, make invasive species a government priority, ensure governments take rapid action to protect nature and our remarkable native wildlife from invasives-led extinction, death and destruction.
If you are having trouble submitting a form, please read this guide.
Please fill out the following form and one of our team will be in contact to assist as soon as possible. Please make sure to include any helpful information, such as the device you were using (computer, tablet or mobile phone) and if known, your browser (Mozilla Firefox, Chrome, Safari etc)
"*" indicates required fields
Dear Project Team,
[YOUR PERSONALISED MESSAGE WILL APPEAR HERE.]
I support the amendment to the Kosciuszko National Park Wild Horse Heritage Management Plan to allow our incredible National Parks staff to use aerial shooting as one method to rapidly reduce feral horse numbers. I want to see feral horse numbers urgently reduced in order to save the national park and our native wildlife that live there.
The current approach is not solving the problem. Feral horse numbers have rapidly increased in Kosciuszko National Park to around 18,000, a 30% jump in just the past 2 years. With the population so high, thousands of feral horses need to be removed annually to reduce numbers and stop our National Park becoming a horse paddock. Aerial shooting, undertaken humanely and safely by professionals using standard protocols, is the only way this can happen.
The government’s own management plan for feral horses states that ‘if undertaken in accordance with best practice, aerial shooting can have the lowest negative animal welfare impacts of all lethal control methods’.
This humane and effective practice is already used across Australia to manage hundreds of thousands of feral animals like horses, deer, pigs, and goats.
Trapping and rehoming of feral horses has been used in Kosciuszko National Park for well over a decade but has consistently failed to reduce the population, has delayed meaningful action and is expensive. There are too many feral horses in the Alps and not enough demand for rehoming for it to be relied upon for the reduction of the population.
Fertility control as a management tool is only effective for a small, geographically isolated, and accessible population of feral horses where the management outcome sought is to maintain the population at its current size. It is not a viable option to reduce the large and growing feral horse population in the vast and rugged terrain of Kosciuszko National Park.
Feral horses are trashing and trampling our sensitive alpine ecosystems and streams, causing the decline and extinction of native animals. The federal government’s Threatened Species Scientific Committee has stated that feral horses ‘may be the crucial factor that causes final extinction’ for 12 alpine species.
I recognise the sad reality that urgent and humane measures are necessary to urgently remove the horses or they will destroy the Snowies and the native wildlife that call the mountains home. I support a healthy national park where native species like the Corroboree Frog and Mountain Pygmy Possum can thrive.
Dear Project Team,
[YOUR PERSONALISED MESSAGE WILL APPEAR HERE.]
I support the amendment to the Kosciuszko National Park Wild Horse Heritage Management Plan to allow our incredible National Parks staff to use aerial shooting as one method to rapidly reduce feral horse numbers. I want to see feral horse numbers urgently reduced in order to save the national park and our native wildlife that live there.
The current approach is not solving the problem. Feral horse numbers have rapidly increased in Kosciuszko National Park to around 18,000, a 30% jump in just the past 2 years. With the population so high, thousands of feral horses need to be removed annually to reduce numbers and stop our National Park becoming a horse paddock. Aerial shooting, undertaken humanely and safely by professionals using standard protocols, is the only way this can happen.
The government’s own management plan for feral horses states that ‘if undertaken in accordance with best practice, aerial shooting can have the lowest negative animal welfare impacts of all lethal control methods’.
This humane and effective practice is already used across Australia to manage hundreds of thousands of feral animals like horses, deer, pigs, and goats.
Trapping and rehoming of feral horses has been used in Kosciuszko National Park for well over a decade but has consistently failed to reduce the population, has delayed meaningful action and is expensive. There are too many feral horses in the Alps and not enough demand for rehoming for it to be relied upon for the reduction of the population.
Fertility control as a management tool is only effective for a small, geographically isolated, and accessible population of feral horses where the management outcome sought is to maintain the population at its current size. It is not a viable option to reduce the large and growing feral horse population in the vast and rugged terrain of Kosciuszko National Park.
Feral horses are trashing and trampling our sensitive alpine ecosystems and streams, causing the decline and extinction of native animals. The federal government’s Threatened Species Scientific Committee has stated that feral horses ‘may be the crucial factor that causes final extinction’ for 12 alpine species.
I recognise the sad reality that urgent and humane measures are necessary to urgently remove the horses or they will destroy the Snowies and the native wildlife that call the mountains home. I support a healthy national park where native species like the Corroboree Frog and Mountain Pygmy Possum can thrive.